
Royal Emblem of Queen Katherine Parr
“Like the family of King Henry’s second wife, the Boleyns, the Parr family had gone up in the world as a result of royal favor and successful marriages.”[3] Historian Agnes Strickland quotes that Katherine’s paternal ancestry was more distinguished than that of Thomas Boleyn and John Seymour. Also, according to David Starkey, Katherine’s lineage, “unlike that of Henry’s second wife, Anne Boleyn, was better and more established at Court.”[3]

Kendal Castle was acquired through the marriage of Sir William de Parr to the heiress and only child of Sir John de Ros of Kendal, Elizabeth de Ros in 1383.
Katherine’s 3x great-grandfather was Sir William Parr (d.1405); in 1383, Sir William de Parre married Elizabeth, only daughter and heiress of Sir John de Ros and Elizabeth le Latimer, daughter of Sir Thomas le Latimer, 1st Baron Latimer of Braybrooke and Lora de Hastings. Elizabeth de Ros was the granddaughter and heiress of Sir Thomas de Ros, Baron of Kendal and had livery of her inheritance. On the accession of the Duke of Lancaster as Henry IV of England, Sir William stood so high in the estimation of the new monarch that he was deputed with the bishop of St. Asaph to announce the revolution to the court of Castile; the King claimed Castile by right of his father, even though his half-sister, Katherine [daughter of the Titular Queen Constanza of Castile], had taken her rightful position as Queen consort after the debate of her Regency. He died on 4 October 1405 being then seized of the fourth part of the manor of Kirby in Kendal. In right of the heiress of Ros and was succeeded by his eldest son, Sir John of Kendal.

Church of St. Peter and St. Paul, Weobley, Hertforshire. Agnes Crophull is buried with her 3rd husband, John Merbery. Her first husband, Sir Walter Devereux, has his own tomb and effigy.
Katherine’s great-great-grandfather, Sir John Parr (b. circa 1383) married to Agnes de Crophull, the sole heiress to Sir Thomas de Crophull of Weobley Castle and Sybil de Bere. Agnes’s grandfather, Sir John of Bonnington was styled Seigneur of Weobley Castle as owner of Weobley Castle in Hertfordshire. The Castle had been gained through his marriage to Margery de Verdun. The Verdun’s descended from John I of England (Joan, Princess of Wales and Llewelyn Ap ‘The Great’, Prince of Wales) and his sister Princess Eleanor, Queen of Castile (Infanta Berengaria of Castile, Queen Consort of Leon and Alfonso IX, King of Leon). They also descended from King David I of Scotland. Agnes was married firstly to Sir Walter Devereux, Sheriff of Herefordshire by whom she had issue. In 1386, Devereux had livery of her lands through which Weobley Castle passed to his children by Agnes. Agnes’s cousin, Sir John de Crophull had Lordship of Ludlow Castle. Her descendants include Anne Devereux (wife of Sir William Herbert, 1st Earl of Pembroke, 1408 creation) and Sir Walter Devereux, 1st Earl of Essex who married to Lettice Knollys. She was also a great-grandmother to Blanche Milbourne, Lady Troy and thus a great-great-grandmother to Blanche Perry. Agnes’s third husband was Sir John Merbury, Chief Justice of South Wales. The couple had no children, however Merbery had issue from his first marriage, Elizabeth, who ended up marrying her step-brother’s son, Sir Walter Devereux. This connection to Agnes Crophull gave the Parr’s more than a few connections to the gentry and courtiers.
Katherine’s great-grandfather, Sir Thomas Parr (b.1407) was Sheriff of Westmorland and Escheator of Cumberland & Westmorland. He married Alice Tunstall, co-heiress of Sir Thomas Tunstall of Thurland Castle and Isabel Harrington. By this connection she was a cousin to Bishop Cuthbert Tunstall who served Henry VIII and all of his children. Under Elizabeth I, he was put under “house arrest” in Lambeth Palace where he died. Isabel Harrington’s sister, Elizabeth, married Sir John Stanley; they were grandparents to Sir Thomas Stanley, 1st Earl of Derby making him a first cousin, three times removed. Derby married Katherine’s great-aunt, Eleanor Neville, by whom he had issue. Upon his second marriage to Lady Margaret Beaufort, Derby became step-father to King Henry VII. Derby was a key figure in the Battle of Bosworth and crowned Henry upon the battlefield. Upon the death of Isabel, Lady Tunstall, Tunstall re-married to Hon. Joan Mowbray, daughter of Sir John de Mowbray, 4th Baron and Hon. Elizabeth Segrave, herself the daughter of Lady Margaret Plantagenet, daughter of Thomas of Brotherton. The marriage produced no children, but the Tunstall’s had step-siblings from Joan’s first marriage to Sir Thomas Grey which included John Grey, Earl of Tankerville.
Katherine’s grandfather, Sir William Parr, was part of King Edward IV’s court. William held the office of comptroller of the household from 1471 to 1475 and again in 1481 till Edward’s death in 1483.[4][5][6] William was held in high favour and close friend to the King and was one of only two courtiers to become Knight of the Garter in the second reign of Edward IV. Elder generations of the Parr family had served in the household of John of Gaunt, 1st Duke of Lancaster, ancestor of Queen Katherine. Sir William Parr could claim royal descent through many lines, a few including:
- Blanche de Brienne and William Fieness, Baron of Tingry; Blanche was the granddaughter of Emperor Jean of Brienne, King of Jerusalem and Infanta Berenguela of León, Empress of Constantinople. By this lineage the Parr’s descended from Eleanor of England, Queen of Castile, daughter of Henry II of England and his consort Eleanor of Aquitaine. By this lineage the Parr’s also descended from the Jimenez Kings of Navarre; the infamous Garcia Ramirez, King of Navarre who “restored” the independence of the Navarrese crown after 58 years of union with the Kingdom of Aragon. The Jimenez dynasty had been ruling Pamplona, later Navarre, since 905 AD. Garcia Ramirez was the grandson of the illegitimate son of Garcia Sanchez III of Navarre. After the assassination of the King’s son, Sancho IV, Navarre was taken over by the Aragonese.
- King John of England [through his illegitimate daughter Joan, Lady of Wales and her husband Llewelyn, Prince of Wales],[1]
- King David of Scotland, sister of Matilda, Queen of the English [thrice through his son Henry, Earl of Huntingdon], [1]
- King William “the Lion” of Scotland [twice through his illegitimate daughter Isabella, Lady Ros],[1]
- Geoffrey Plantagenet, founder of the Plantagenet Kings of England through several lines.[1]
- King Henry I of England via several illegitimate children such as Robert de Caen, 1st Earl of Gloucester
- Stephen Blois, Count of Aumule.
- Several times by Henry I, King of France
- Adela of England and Stephen of Blois
- Adeliza of Louvain, Queen consort of the English
- The Brus family from which came Robert de Brus, King of the Scots.[1]

Lady Joan Beaufort and her daughters
Katherine descended from every King of England who had issue up to King Edward III. Katherine Parr was also the only queen of King Henry VIII to descend from the Beaufort’s; the illegitimate, later legitimized issue of Prince John of Gaunt, 1st Duke of Lancaster and his third wife, Katherine Swynford Roet. King Henry’s first wife, Katherine of Aragon, also descended from John of Gaunt by his first two wives.

Ravensworth Castle, ancestral home to the Barons FitzHugh
Sir William Parr’s wife, the Hon. Elizabeth FitzHugh, was the daughter of Henry, 5th Baron FitzHugh of Ravensworth Castle and Lady Alice Neville. FitzHugh, himself, descended from Henry I (several times), Henry II, and John I (twice); all from illegitimate children. His family was an old baronial family of England descending from Akarius Fitz Bardolph, Lord of Ravensworth (d.1161), the son of Bardolph an 11th century nobleman living in Richmondshire, the area encompassing the Ure, Tees and Swale valleys in northern England.[5] The 5th Baron was the son of William, 4th Baron FitzHugh and Margery Willoughby; by his mother he was a nephew of Richard Willoughby, 6th Baron Willoughby of Eresby.
Lady Alice was sister to Richard Neville, 16th Earl of Warwick and 6th Earl of Salisbury [best known as “Warwick, the Kingmaker”] and other prominent noblemen and women. Her cousin, Sir George Neville, 1st Duke of Bedford was intended to marry Elizabeth of York [mother of King Henry VIII]; this obviously fell through due to his father and nephew’s [Warwick] rebellion against Edward IV. The Neville’s were already established at court being grandchildren of John of Gaunt’s legitimized daughter Lady Joan Beaufort, Countess of Westmorland. Katherine was just about related to every noble and royal at court who came before or during her time; Edward IV and Richard III were first cousins (thrice removed of Katherine Parr). Their wives, Queen Anne Neville and Queen Elizabeth Woodville, were also a first cousins. [The Woodville connection comes from Katherine’s mother, Maud Green — Queen Elizabeth was a first cousin, thrice removed of Katherine]. This connection made her related to all of her husbands in one way or another.

Sir Thomas Montacute, 4th Earl of Salisbury and Lady Eleanor Holland

Princess Joan of Acre, eldest daughter of Edward I and Eleanor of Castile
Lady Alice Neville’s mother Lady Alice Montacute was suo jure 5th Countess of Salisbury being the only surviving child of Sir Thomas, 4th Earl of Salisbury and Lady Eleanor Holland [pictured above]. Salisbury married to Alice Chaucer. Salisbury descended from:
- Princess Joan of Acre, eldest daughter of King Edward I and his first wife, Eleanor of Castile,
- Henry I of England by his illegitimate sons Robert de Caen, 1st Earl of Gloucester [twice] and Reynold of Dunstanville, 1st Earl of Cornwall,
- William the Lion, King of Scots by his illegitimate daughter Isabella, Lady Ros,
- William the Conqueror by his illegitimate son William Peverell and legitimate daughter, Adela of Normandy.
Lord Salisbury’s siblings included Lady Anne who married thrice. By her marriage to Sir Richard Hankford they were ancestors to Anne Boleyn. After being widowed, she became Duchess of Exeter as wife to the 2nd Duke of Exeter (nephew of the 2nd Earl of Kent, ancestor to Queen Katherine Parr).
Lady Eleanor Holland descended from

Coat of arms of Prince Edmund of Woodstock, 1st Earl of Kent
- Edward I of England by his son from his second marriage to Marguerite of France [daughter of Philip III of France and Maria of Brabant], Edmund of Woodstock, 1st Earl of Kent,
- Henry III of England by his son Prince Edmund, 1st Earl of Lancaster [whose wife was Blanche of Artois, Queen of Navarre and mother to another of Queen Katherine’s ancestors, Jeanne I, Queen Regnant of Navarre]. Their son was Sir Henry, 3rd Earl of Lancaster who married Maud Chaworth [descendant of Louis VI of France],
- John I of England twice by his illegitimate daughter Lady Joan, Lady of Wales,
- Henry II of England by his legitimate daughter by Queen Eleanor of Aquitaine, Eleanor of England, Queen of Castile and by his illegitimate son William Longespee, 1st Earl of Salisbury,
- Henry I of England twice by his illegitimate daughter Lady Maud of Normandy, Duchess of Brittany and twice by his illegitimate son, Robert de Caen, 1st Earl of Gloucester,
- Duncan II of Scotland by his son the Earl of Moray
- David I of Scotland, twice by his son Henry, Earl of Huntingdon,
- Louis VI of France by his son Pierre of Courtenay,
- Geoffrey Plantagenet twice by his son Sir Hamelin Warrenne, Earl of Surrey,
- William, the Conqueror twice by his daughter Adela of Normandy and his illegitimate son William Peverell.

Coat of arms relating to those mentioned below who are members of, descendants of, or married into the Holland family. L to R: Mortimer, 2nd Earl of Kent, 1st Duke of York, 3rd Earl of Cambridge, Duke of Clarence, 3rd Duke of Lancaster, 16th Earl of Warwick
Lady Salisbury’s siblings included:
- Lord Thomas Holland, 1st Duke of Surrey, 3rd Earl of Kent.
- Lord Edmund of Woodstock, 4th Earl of Kent who had a child by Lady Constance of York, daughter of Edmund of Langley, Duke of York (husband of his sister, Lady Joan). In 1403, there was a betrothal of Lord Edmund of Woodstock to Lady Constance of York; not apparent as to whether or not they actually married. [Richardson, Plantagenet Ancestry]
- Lady Elizabeth who married Sir John Neville; ancestors to the Earls of Westmorland (Neville was the heir to the 1st Earl and his first wife Lady Margaret Stafford. The Earl would later marry Lady Joan Beaufort — the two were ancestors to Queen Katherine Parr).
- Lady Joan married to Edmund of Langley, Duke of York — no issue. Nevertheless she was styled Duchess of York.
- Lady Alianore, Countess of March, wife to the 4th Earl of March — and through them the crown of Edward IV was claimed by their daughter, Lady Anne Mortimer, Countess of Cambridge (wife of Richard of York, 3rd Earl of Cambrige, brother to Lady Constance of York). The Countess would marry again to the 5th Baron of Powis, their grandson would marry the illegitimate daughter of the Duke of Gloucester (son of King Henry IV), Lady Antigone.
- Lady Margaret, Countess of Somerset and Duchess of Clarence married John Beaufort, 1st Earl of Somerset (illegitimate son of John of Gaunt by Katherine Swynford) and by him they were ancestors to Lady Margaret Beaufort, mother of Henry VII. Margaret would re-marry to Thomas of Lancaster, Duke of Clarence, grandson of John of Gaunt by his son King Henry IV.

Princess Joan of Kent and her son, King Richard II
Lady Salisbury’s [Lady Eleanor Holland] paternal grandmother was Princess Joan of Kent, suo jure 4th Countess of Kent and later Princess of Wales. Her story is one of interest. She married firstly to Sir Thomas Holland who became 1st Earl of Kent through her inheritance. By him she had Lady Salisbury’s father, Sir Thomas Holland, 2nd Earl of Kent. Her uncle was Sir John, 1st Duke of Exeter who married Lady Elizabeth of Lancaster, daughter of Prince John of Gaunt and his first wife, Blanche of Lancaster. They were parents to John Holland, 2nd Duke of Lancaster who married thrice; Lady Anne Stafford, Beatrice of Portugal, and Lady Anne Montacute. His second wife, Beatrice of Portugal was half-sister to Edward I of Portugal; John, Lord of Reguengos de Monsaraz; and Afonso, Duke of Braganza. Lord of Reguengos was a grandfather to Queen Isabella of Castile (mother of Queen Katherine of Aragon) while the Duke of Braganza was a great-grandfather.
Lady Salisbury’s paternal aunts were Lady Joan, Duchess of Brittany [wife to John V of Brittany] and Lady Maud, Countess of Ligny [wife to Waleran III of Luxembourg; their daughter Jeanne married Antoine de Valois, Duke of Brabant]. Joan of Kent’s third marriage was to Edward, Prince of Wales [eldest son and heir of King Edward III]; their son was King Richard II of England and thus granduncle to Lady Salisbury.

John Holland, 1st Duke of Lancaster.
Lady Salisbury’s maternal grandparents were Sir Richard “Copped Hat” FitzAlan, 10th Earl of Arundel and Lady Eleanor of Lancaster, daughter of the 3rd Earl of Lancaster and his wife, Maud Chaworth. The Earl and Countess were parents to Lady Alice FitzAlan, Countess of Kent (wife to the 2nd Earl). By her mother, Lady Kent had half-siblings by Lady Arundel’s first marriage to Sir John Beaumont, 2nd Baron; Maud, the ancestress of the Courtenay Earls of Devon and Lord Henry (who were both half-siblings themselves to Sir William Devereux, father of Sir Walter, first husband to Agnes Crophull, later Lady Parr of Kendal as wife to Sir John Parr.) Lady Kent’s siblings included:
- Lady Joan of Arundel, mother to the uncrowned Mary de Bohun, wife of Henry IV and mother to Henry V. Her other daughter became Duchess of Gloucester as wife to Lord Thomas of Woodstock, Duke of Gloucester, youngest son of King Edward III.
- Sir Richard, 11th Earl of Arundel who’s daughter Margaret became Duchess of Norfolk; another daughter Joan became Lady Bergavenny, ancestress to Lords Bergavenny, Earls of Shrewsbury, and grandparents to the 7th Earl of Ormonde (ancestor of Queen Anne Boleyn).
- Sir John, 1st Lord Arundel — ancestor to the later Earls of Arundel and Dukes of Norfolk. Lord Arundel’s great-grandson married Lady Joan Neville, sister of “Warwick, the Kingmaker” and Alice (great-grandmother to Queen Katherine Parr).
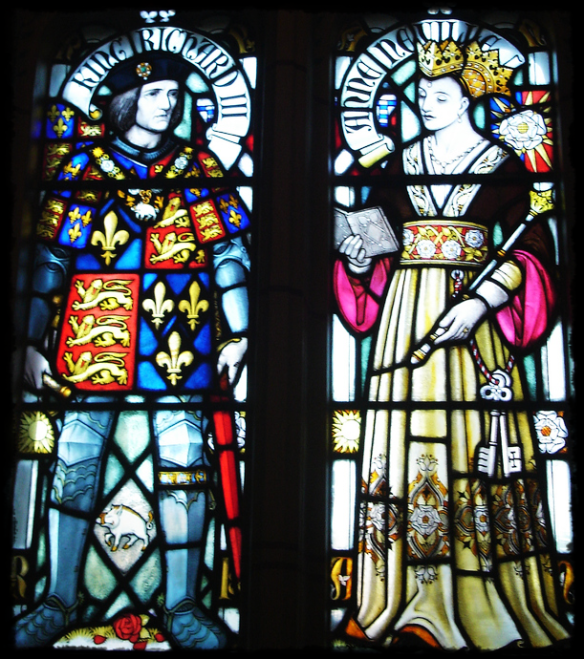

King Richard III and consort Lady Anne Neville were both cousins to Queen Katherine’s paternal grandmother
When the Duke of Gloucester became King in 1483, as Richard III, both Elizabeth and her mother Alice were appointed ladies-in-waiting to Alice’s niece, queen consort Lady Anne Neville. The profession would span five generations down to Katherine’s sister, Anne, who would serve all six of King Henry VIII’s wives. by Lady Parr (Golden Aged writer)
Katherine’s father, Sir Thomas Parr, was a close friend of King Henry VIII; Parr’s step-father, Sir Nicholas Vaux, had been educated in the household of Lady Margaret Beaufort, Henry’s grandmother, where Parr is also believed to have spent some time. Sir Thomas was present at court and was in the circle of Henry VIII which included Sir Thomas Boleyn. Both were knighted in 1509 at Henry’s coronation; Parr was also made a Knight of the Garter and appointed Sheriff of Northamptonshire on that occasion. Parr became Master of the Wards and Comptroller of the household of Henry VIII. Parr’s brother, William [later Baron Parr of Horton], was also a part of the King’s circle. They kept company with the Stafford’s and their cousins, the Neville’s. They were also friend’s with the Carew’s and Sir Thomas Boleyn, father Queen Anne Boleyn. In 1515, Parr was entrusted with escorting Queen Margaret of Scotland [the king’s elder sister] from Newcastle back to London.
The “lowly” marriage of Mary Boleyn to Sir William Stafford — unlike “The Tudors” insistence that he was a “nothing” — Stafford was actually the grandson of Sir John Fogge and Alice Haute (cousin to Queen Elizabeth Woodville). This connection made Stafford a cousin to Parr’s mother, Maud Green (her aunt was Stafford’s mother, Margaret).
Katherine’s brother, William, entered the household of Henry Fitzroy, the King’s illegitimate son, at the age of eleven. It was there that he met Henry Howard, Earl of Surrey. They were educated together and Katherine’s uncle, Sir William, Baron Parr of Horton, was part of the head of the household for Fitzroy.
From Sir Thomas’ grandmother to his own daughter, Anne, were all ladies-in-waiting to the queens of England. His grandmother and mother both personally served under special appointment by Richard III’s consort herself, Lady Anne Neville. Anne was the niece of Parr’s grandmother, Lady Alice Neville. Katherine’s sister, Anne Parr [Herbert], was one of the few women to serve all six of Henry’s wives. Maud Parr nee Green, his wife, was good friend’s with Queen Katherine of Aragon and a lady-in-waiting to her. She was given private chambers next to the queen’s and Queen Katherine was supposedly Katherine Parr’s godmother. Lady Parr’s grandmother, Lady Alice Fogge (Haute) was a lady to Queen Elizabeth Woodville (see below).
If Sir Thomas had not died at such an early age he would have been given the title which his brother received or another barony. He was also co-heir to the FitzHugh barony; which is still in abayence between the descendants of his aunt Alice FitzHugh, Lady Fiennes and his daughter, Anne Parr, Countess of Pembroke.
Green Family
Katherine’s mother also descended from royal blood. Maud Green’s family had long served the crown.
Sir Henry Green (died 6 August 1369) was an English lawyer, and Chief Justice of the King’s Bench from 24 May 1361 to 29 October 1365. Early in his career he served both Queen Isabella (consort of Edward II) and Edward the Black Prince. He was made justice of the Court of Common Pleas in 1354, and knighted by King Edward III.
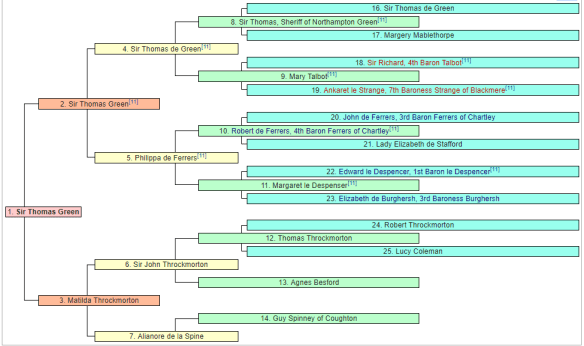
By her grandfather, Sir Thomas Greene of Greens Norton, Queen Katherine directly descended from King Fergus of Galloway and many nobles and Kings of England which included William the Conqueror, John of England, Henry I by three illegitimate children and Empress Matilda, Edward I, and Henry II of England by two legitimate children and one illegitimate. By both husbands of Isabella of Angoulême, Queen Consort of England; from Welsh nobility like Nest Ferch, Princess of Wales, Llewelyn Ap ‘The Great’, Gwladys Dhu verch; Spanish royals such as Alfonso II of Aragon, Alfonso IX of Aragon; they also descended from French royalty Charles I, Henry I, Louis VII of France and Scottish royals such as David I, Maud of Huntingdon; and from Jean of Brienne, King of Jerusalem through her connections with the Ferrers of Groby, Talbot, Despencer, FitzAlan, De Clare, Earls of Ormonde, and other noble families.
By her mother, Joan Fogge, Lady Parr was a cousin to Elizabeth Woodville, queen consort of Edward IV; descending from Queen Elizabeth’s grandfather, Sir Richard Woodville. When Elizabeth became queen to Edward IV, she brought her favorite female relatives to court to serve her. Lady Parr’s grandmother, Lady Alice Fogge (born Haute), was one of five ladies-in-waiting to her cousin Elizabeth Woodville in the 1460s.[4]
Relations to Husbands
Queen Katherine and Henry VIII’s closest relations: Third cousins (through Sir Richard Wydeville and Joan Bedlisgate); third cousins once removed (through Ralph Neville, 1st Earl of Westmorland and Lady Joan Beaufort); and double fourth cousins once removed (through Thomas Holland, 2nd Earl of Kent and Lady Alice FitzAlan and John of Gaunt, 1st Duke of Lancaster and Katherine Swynford). Queen Katherine also shared ancestors with her 4th husband, Thomas Seymour, but the closest one is Edward III and Philippa.
Sources:
- Douglas Richardson. “Plantagenet Ancestry,” 2005.
- Douglas Richardson. “Magna Carta Ancestry,” 2nd Edition, 2011.
- David Starkey. “Six Wives: The Queens of Henry VIII,” HarperCollins, May 4, 2004. pg 690. Google eBook.
- Barbara J. Harris. “English Aristocratic Women, 1450-1550 : Marriage and Family, Property and Careers: Marriage and Family, Property and Careers,” Oxford University Press, Jul 26, 2002. pg 218.
- John Burke. “A general and heraldic dictionary of the peerages of England, Ireland, and Scotland, extinct, dormant, and in abeyance,” 1831.
Some of her ancestry can be viewed here:
Tudors Wiki: Ancestry of Queen Catherine Parr
Thoroughly researched. One line still in question: Sir Roger, 4th Baron Strange of Knockyn’s wife, Maud, who has been theorized as the illegitimate daughter of Enguerrand VII de Coucy, 1st Earl of Bedford which would relate her back to ancestors like the Habsburgs; the Chatillions; the Wittlesbachs; Beatrice of England, Duchess of Brittany [daughter of Henry III of England and Eleanor of Provence]; Matilda of England, Duchess of Saxony [daughter of Henry II of England and Eleanor of Aquitaine]; the Champagne and Jiminez Kings of Navarre; and more.





















![Bishop Cuthbert Tunstall [right] confronts Katherine of Aragon in "The Tudors".](https://tudorqueen6.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/09/bishop-cuthbert-tunstall1.png?w=584)



![De arte supputandi libri quattuor Cuthbert Tunstall London: R. Pynson, 1522 [DeM] L.1 [Tunstall] SSR](https://tudorqueen6.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/09/tunstall-book.jpg?w=584)





























