Effigy of John Neville, 4th Lord. By jmc4 – Church Explorer
Sir John Neville, 4th Baron Latimer of Snape Castle (1520[1][2] – 22 April 1577) was an English nobleman of the powerful House of Neville.
Early life
Born about 1520 (he was 23 when his father died, 2 March 1543), he was the only son of John Neville, 3rd Baron Latimer of Snape Castle and his first wife Dorothy, sister and co-heiress of John de Vere, 14th Earl of Oxford. After the death of his mother, Lord Latimer married secondly, Elizabeth Musgrave, by whom he had no children. After her death in 1530, Latimer married again in 1534 the widowed Katherine, Dowager Lady Borough [Parr].
From the beginning of his father’s marriage to Katherine, she tried to be a good step-mother to both children, but John proved to be difficult. There is some indication that Margaret, his sister, was their father and Katherine’s favourite. If that is true, it may explain the turbulence which would follow as John got older. As a “teenager”, John proved to be a confident sulking, lying, and over-sensitive boy. Lord Latimer did not name his son as heir to his properties and made sure that his son could not meddle with his inheritance or father’s legacy. In Lord Latimer’s will, Katherine was named guardian of his daughter and was put in charge of Lord Latimer’s affairs which were to be given over to his daughter at the age of her majority.
In January 1537, John, his sister Margaret, and step-mother Katherine, were held hostage at Snape Castle during the uprising of the North. The rebels ransacked the house and sent word to Lord Latimer, who was returning from London, that if he did not return immediately they would kill his family. When Lord Latimer returned to the castle he somehow talked the rebels into releasing his family and leaving, but the aftermath to follow with Lord Latimer would prove to be taxing on the whole family.[3]
Later life
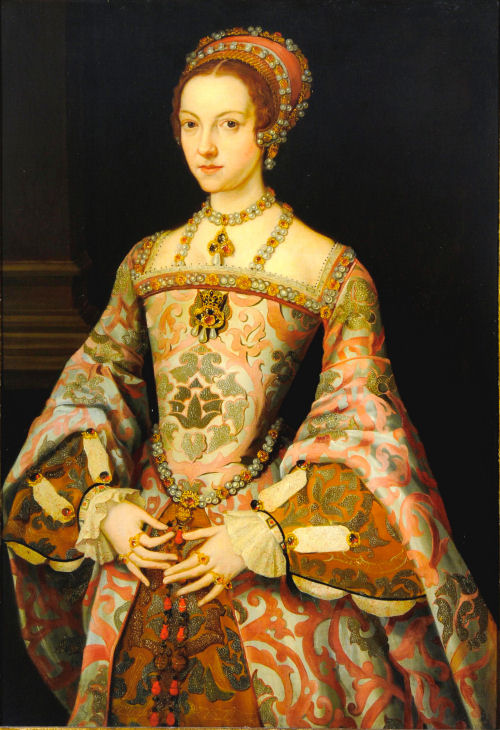
Nevill became Baron Latimer on his father’s death in 1543. Although the relationship proved difficult during his youth, Katherine, did not forget Nevill. Katherine stayed close with her former stepchildren. In fact, Katherine made John’s wife, Lucy Somerset, a lady-in-waiting when she became queen consort to King Henry VIII.[1][3]
In May 1544, Nevill was involved with the siege of Edinburgh in Scotland and it was there that he was knighted. Nevill then went to war in France where he took part in the siege of Abbeville.
John became an emotionally unstable man later in life. In the summer of 1553, John was sent to Fleet Prison on charges of violence done to a servant. He was arrested for attempted rape and assault in 1557 and in 1563, he killed a man. Of the situation in 1553, Thomas Edwards wrote to the Earl of Rutland describing the violence which had taken place with the servant quoting “too great a villainy for a noble man, my thought.” That this public violence occurred after the death of his step-mother, Katherine, might suggest that at least she had some sort of control over Nevill while she was alive.[3]
Marriage and issue
In 1545, Latimer married Lady Lucy Somerset, daughter of Henry Somerset, 2nd Earl of Worcester and his second wife, Elizabeth Browne.[4] The new Lady Latimer was a cousin to Queen Katherine as the great-granddaughter of the Marquess of Montagu, brother to Lady Alice FitzHugh [great-grandmother of Queen Katherine]. Lady Lucy became a lady-in-waiting to her husband’s former step-mother, Queen Katherine Parr.
Together they had four daughters that all produced children by their first marriages:
- Hon. Elizabeth Neville (c. 1545 – 1630), married firstly Sir John Danvers of Dauntsey, and secondly Sir Edmund Carey. Elizabeth’s descendants by Danvers included the Dukes of Leeds [extinct in 1964]; Earls of Lichfield; Earls of Leicester of Holkham from which Sarah of York descends.
- Hon. Katherine Neville (1546 – 28 October 1596), married firstly Henry Percy, 8th Earl of Northumberland, and secondly Francis Fitton of Binfield. Lord and Lady Northumberland were parents to Sir Henry, 9th Earl of Northumberland. Her descendants include Lady Diana Spencer, Princess of Wales; HM Queen Elizabeth II by her mother; Sarah, Duchess of York; and others. Katherine was buried in the Chapel of St. Nicholas in Westminster Abbey, within the Percy family, Dukes of Northumberland.
- Hon. Dorothy Neville (1547 – 23 March 1609), married Sir Thomas Cecil, Queen Elizabeth’s counselor, later Earl of Exeter. Cecil was the half-brother of the Earl of Salisbury. Her descendants also include Lady Diana Spencer, Princess of Wales.

Latimer’s daughter, the Hon. Dorothy Neville who became Countess of Exeter when her husband Thomas Cecil was elevated to Earl in 1605
- Hon. Lucy Neville (c. 1549 – April 1608), married Sir William Cornwallis of Brome Hall. Their daughters made advantageous marriages to nobility such as the marriage of their daughter Anne to the 7th Earl of Argyll by whom she had issue. Another daughter, Elizabeth, became Viscountess Lumley as the wife of Sir Richard, 1st Viscount Lumley.
Lord Latimer died without sons in 1577; his four daughters became his joint heiresses. The barony became abeyant until 1913, when its abeyance was terminated in favour of Latimer’s distant descendant Francis Money-Coutts, 5th Baron Latymer.

Effigy and tomb of the 4th Lord Latimer in Nevilles’ Chapel, Wells, North Yorkshire Well Village Website © Well Parish Council 2011
He was buried in St. Michael’s Church, Well, North Yorkshire which adjoined Neville’s home, Snape Castle. The church had a long standing history with the Neville family going back to John and Queen Katherine Parr’s ancestor, Sir Ralph Neville, the 1st Earl of Westmorland. Westmorland married Lady Joan Beaufort; the only daughter of Prince John of Gaunt, 1st Duke of Lancaster by his mistress, later wife, Katherine Roet. Ralph was responsible for the building of the present church c. 1330. Latimer’s mural monument lies in Nevilles’ Chapel within Well’s Church. Latimer’s daughter, Hon. Dorothy, Countess of Exeter inherited Snape Castle and is also buried there with her husband Thomas Cecil, 1st Earl of Exeter.[5] According to a card placed upon the tomb, the four coat of arms on his tomb represent that of his four daughters and their husband.
His wife, Lucy, was buried in Hackney Parish Church in London. Her grand tomb has her effigy surrounded by her four daughters.[6] Her tomb is one of only a few in England which feature such noble bearings; the other being the tomb of George Clifford, Earl of Cumberland at Skipton which is surrounded by no fewer than seventeen richly adorned shields which include that of Brandon, Dacre, de Clare, St. John, and more.[7] The Earl himself was a descendant of Katherine Parr’s great-aunt, Mabel Parr, Lady Dacre. Lady Latimer’s tomb not only includes the arms many of those on Clifford’s tomb as Neville, Beauchamp, Dacre, Berkeley, and Percy but also those of de Vere Earl of Oxford, Walcot, and Cecil.[6] Lord Latimer’s arms (the Neville) are at one end of the tomb. The statues of the four daughters were two on each side of the monument; at the side of each the shield of the husband impaling the Neville arms. These arms are thus repeated five times. At the other end are Lady Latimer’s arms: the lions and fleur de lis that is France and England, quarterly, the arms of the Dukes of Beaufort, descended from the eldest legitimated son of John of Gaunt, her father being Henry Somerset, 2nd Earl of Worcester.[6]

Document on the magnificent tomb of Lady Lucy Somerset, Lady Latimer; wife of the 4th Lord Latimer and lady to HM Queen Katherine Parr. Courtesy of JMC4 Church Explorer.[8]
“The effigy of Lady Latimer was exquisitely sculptured and was fixed on the top of the table monument She appears to be dressed in a scarlet robe with a coronet on her head and the other part of the dress was richly gilt This effigy was probably intended for a portrait of her.”[6]
Her epitaph reads:
Such as she, is such surely shall yee bee; Such as shee was, such if yee bee, be glad: Faire in her youth though fatt in age she grew; Virtuous in bothe whose glosse did never fade. Though long alone she ledd a widowe’s life, Yet never ladye live da truer wife. From Wales she sprang, a Branch of Worcester’s race, Grafte in a stock of Brownes her mother’s side: In Court she helde a maide of honor’s place, Whilst youth in her, and she in Court did byde. To John, Lord Latimer, then became she wife; Four daughters had they breathing yet in life. Earl of Northumberland tooke the first to wife; The nexte the heire of Baron Burleigh chose: Cornwallis happ the third for terme of life: And Sir John Danvers pluckt the youngest Rose. Their father’s heirs, them mothers all she sawe: Pray for, or praise her: make your list the Lawe, Made by Sir William Cornwallis, Knight, this Ladye’s Sonne in Lawe.[6]
Ancestry
By his father, Latimer descended from King Edward III of England twice. Latimer’s great-grandparents were Sir Henry Neville, heir to the barony of Latimer and Earldom of Warwick, and the Hon. Joan Bourchier. Neville was a grandson of Sir Ralph Neville, 1st Earl of Westmorland and his second wife, Lady Joan Beaufort. Lady Joan was the legitimized daughter of Prince John of Gaunt, Duke of Lancaster by his mistress, later wife, Katherine Roet. Bourchier was a granddaughter of Sir William, 1st Count of Eu and Lady Anne of Gloucester, daughter of Prince Thomas of Woodstock [youngest son of Edward III] and his wife, Lady Eleanor de Bohun. This connection to the Bourchier family made Latimer a cousin of the Earls of Bath, Lords Dacre of the South, the Lady Margaret Bryan [governess of the King’s children], Lady Anne Bourchier [husband of Katherine Parr’s brother William Parr], and even the Duchess of Somerset Anne Stanhope.
Latimer’s mother was the granddaughter of the 12th Earl of Oxford and Elizabeth Howard. Oxford was himself a descendent of Edward I of England and Eleanor of Castile by their daughter Princess Joan of Acre. The Countess of Oxford, Elizabeth Howard, was a descendant of John I of England by his son Richard of England, Earl of Cornwall, King of the Romans as well as a descendant of Henry I’s illegitimate son Reynold de Dunstanville, 1st Earl of Cornwall.
References
- ^ Linda Porter. Katherine the Queen; the Remarkable Life of Katherine Parr, the Last Wife of Henry VIII. Macmillan, 2010. pg 66-67.
- According to Linda Porter’s Katherine, the Queen, Neville was 14 at the time of his father’s marriage to Catherine Parr.
- Susan E. James. Catherine Parr, Henry VIII’s Last Love. The History Press, 2009.
- G. E. Cokayne. The Complete Peerage of England, Scotland, Ireland, Great Britain, and the United Kingdom, Vol. VIII, G. Bell & sons, 1898. pg 200. Google eBook
- Village of Well, North Yorkshire, http://www.wellvillage.org.uk/history/
- Richard Simpson. Some Accounts of the Monuments in Hackney Church, Billing and Sons, 1881; Chapter: Lady Latimer.
- W. Harbutt Dawson. History of Skipton, Simpkin, Marshall, London, 1882.
- JMC4 Church Explorer . London, Hackney, Flickr, 2008.
- T. Fisher. Hackney Council, The Churchyard Memorials: Memorial to Lady lucy Latimer in the old church, c.1795.
Written and researched by Meg McGath
27 August 2012







![Bishop Cuthbert Tunstall [right] confronts Katherine of Aragon in "The Tudors".](https://tudorqueen6.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/09/bishop-cuthbert-tunstall1.png?w=584)



![De arte supputandi libri quattuor Cuthbert Tunstall London: R. Pynson, 1522 [DeM] L.1 [Tunstall] SSR](https://tudorqueen6.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/09/tunstall-book.jpg?w=584)