From Sex and Sleaze: Time Traveller’s guide to Tudor England:
Childbirth is an exclusively female affair, with only female midwives in attendance and no doctors. After childbirth, babies are rapidly baptised because of high infant mortality, usually in the absence of their mothers. New mothers are not allowed in church until about 30 days after the birth, and then must be ‘churched’, or ritually purified.
In December of 1547, Queen Katherine Parr became pregnant for what most people believe to be the first time by her fourth and final husband, Sir Thomas Seymour. After four husbands and twenty years of marriage, Katherine was about to fulfill what she felt was the primary duty of a wife, to give birth to a healthy baby; boys being preferred in aristocratic circles. Like today, some titles still cannot be inherited by the eldest or only daughter of a peer; meaning a girl cannot inherit the title of her father which is usually then passed to the closest living male relative, that being usually an uncle or cousin.
Queen Katherine found pregnancy difficult. She still had an on-going feud with her brother-in-law, the Lord Protector and his rather nasty wife, had morning sickness, was constantly worrying about her step-daughter Lady Elizabeth, and the temper of her husband and lack of discretion towards his feelings for Lady Elizabeth must have made the early months of pregnancy extremely hard for the Queen Dowager.[1] In 1549, after the death of the Queen, two cramp rings for use against the pains of childbirth and three pieces of unicorn horn, sovereign remedy for stomach pains, were found in the chest of Katherine’s personal belongings which were talismans most likely from her husband and friend’s to alleviate the pains of childbirth and anticipated pangs of childbirth. Katherine was almost thirty-six, an advanced age to begin a pregnancy. The emotional strain of her household with Seymour’s infatuation with Lady Elizabeth couldn’t have helped her early months either.
As Katherine’s pregnancy progressed, her involvement in politics, if not her interest, diminished. She viewed her approaching motherhood with delight despite knowing the risks and the possibility that death in child birth was a very real possibility.
In June Katherine wrote to her husband from Hanworth:
“I gave your little knave your blessing, who like and honest man stirred apace after and before. For Mary Odell being abed with me had laid her hand upon my belly to feel it stir. It hath stirred these three days every morning and evening so that I trust when ye come it will make you some pastime.”[2]

The Dowager Queen’s letter from Hanworth which is preserved at Sudeley Castle © Meg McGath, 2012.
Seymour, who was also aware of the perils of childbirth — from his own sister’s account — replied from Westminster:
“I do desire your highness to keep the little knave so lean and gaunt with your good diet and walking, that he may be so small that he may creep out of a mousehole. I hear my little man doth shake his poll [head], [and] trusting God should give him life to live as long as his father, he will revenge such wrongs as neither you nor I can.”[3]
The last part of the message obviously had to do with Seymour’s friction with his elder brother which at this time was on the verge of paranoia.

The Ruins of the 15th Century State Apartments, where Katherine would have spent her last few months © Meg McGath, 2012.
Seymour decided that Katherine should be confined as far away possible from the press of business and turmoil of the court as well as the summer plagues of London. Katherine was taken to Sudeley Castle in Winchcombe, England, outside of Cheltenham. The castle has a long history stretching back to William de Tracy. Richard III used the castle as campaign headquarters during the Battle of Tawkesbury; in which Katherine’s grandfather fought. Upon the death of Richard III, the castle reverted to the crown and new monarch, Henry VII; who gave the castle to his uncle, Jasper Tudor. After the death of Jasper Tudor, Sudeley reverted to the crown again, to King Henry VIII. In fact, the King made a visit to the castle with Anne Boleyn in 1535. Upon the ascension of Edward VI, Sir Thomas was created Lord Seymour of Sudeley and was granted the castle. In preperation for her lying-in, Seymour spent 1,000 pounds having the rooms prepared for her in his newly aquired house at Sudeley in Gloucestershire.[4] With beautiful gardens and walks, the castle would have been a perfect place for Katherine to spend the last three months of her pregnancy.

The Nursery at Sudeley Castle
On Wednesday, 13 June 1548, Seymour accompanied his wife, who was now six months pregnant, and his young ward, Lady Jane Grey, from Hanworth to Sudeley Castle in Gloucestershire. Lady Elizabeth Tudor had been sent away that Spring so she did
not accompany them. In this castle, Katherine spent the last three months of her pregnancy and the last summer of her life. Typical of Queen Katherine, she spared no expense when it came to attendants. She was attended by her old friend and doctor, Robert Huicke, and was surrounded by other old friends, Miles Coverdale, her chaplain, her almoner, John Parkhurst, Sir Robert Tyrwhitt, and the ladies who had been with her over the years such as Elizabeth Trywhitt and Mary Wodhull. Katherine also had a full compliment of maids-of-honour and gentlewomen as well as 120 gentlemen and yeomen of the guard. In spite of his duties, Sir Thomas Seymour seems to have spent most of that summer with his wife. Katherine whiled away her summer days overseeing the education of Lady Jane Grey while preparing for her baby. Her affections for her husband seemed as strong as ever, as was her belief in the final analysis, Seymour would make the moral choice over the immoral one.
The queen wrote to her husband who had been called away on duty describing the baby as very active.
“I gave your little knave your blessing, who like an honest man stirred apace after and before. For Mary Odell being abed with me had laid her hand upon my belly to fell it stir. It hath stirred these three days every morning and evening so that I trust when you come it will make you some pastime…”
It was during this time that the queen dowager reconciled with Lady Mary who wrote to her stepmother on 9 August:
“I trust to hear good success of your Grace’s great belly; and in the meantime shall desire much to hear of your health, which I pray almighty God to continue and increase to his pleasure as much as your own heart can desire.”[6]
The Lady Elizabeth, who was now living away from her step-mother also wrote, too, answering a letter of Katherine’s in which the queen described the beauties of Sudeley and wished the princess with her once more:
“Although your Highness’ letters be most joyful to me in absence, yet considering what pain it is to you to write, your Grace being so great with child, and so sickly, your commendation were enough in my Lord’s letter. I much rejoice at your health with the well liking of the country. Your Highness were like to be cumbered, if I should not depart, till I were weary being with you; also it were in the worst soil in the world your presence would make it pleasant… God send you a most lucky deliverance.”[7]
One could reflect on this letter — seeing Lady Elizabeth’s concern when it came to childbirth. Perhaps this weariness and the eventual death of her beloved step-mother would confirm that she would never consider having children.

Queen Katherine looks from the window in her nursery which overlooks the gardens and Chapel.
While Katherine awaited her confinement, Katherine continued decorating the nursery which overlooked the gardens and the Chapel. The nursery of an expected heir was done up in crimson and gold velvet and taffeta, with furniture and plate enough for a royal birth. In Seymour’s eyes, the child would be a member of the royal family as Katherine was still officially the only queen in England. After his daughter’s birth, Seymour was overheard telling Sir William Sharington that,
“it would be strange to some when his daughter came of age, taking [her] place above [the duchess of] Somerset, as a queen’s daughter.”[5]
Besides the baby’s cradle was a bed with a scarlet tester and crimson curtains and a separate bed for the nurse.

The Queen’s Garden where Katherine would have walked.
The Queen continued to take the advice of her doctor and walked daily among the grounds of Sudeley, but she was still concerned about the politics and overseeing of the new boy king.
On Thursday, 30 August, [coincidentally in 2012, the celebration of Queen Katherine’s 500th anniversary of her birth, the 30th of August
ALSO fell on a Thursday, on the eve of a blue moon] Katherine brought to bed a healthy baby girl who was named Lady Mary in honour of her step-sister, the Lady Mary Tudor. Disappointed briefly that the son and avenger he had hoped for had turned out to be a girl, Seymour rallied quickly and announced his daughter’s birth to the lord protector in ‘glowing terms’ and with a detailed description of her beauty. Somerset, the father of 12, was amused by his brother’s enthusiasm for fatherhood. But Seymour’s joy in his child’s birth was followed by fear at his wife’s worsening condition.

This portrait of a baby/small child hangs in the Nursery at Sudeley Castle. No identification.
Links
Sources:
- Linda Porter. ‘Katherine, the queen,’ Macmillan, 2012.
- Susan James. ‘Catherine Parr: Henry VIII’s Last Love,’ The History Press, Gloucestershire, 2008, 2009 [US Edition].
- Janel Mueller. ‘Katherine Parr: Complete Works and Correspondences,’ University of Chicago Press, Jun 30, 2011.
- Emma Dent. ‘Annals of Winchcombe and Sudeley,’ London, J. Murray, 1877. Out of copyright; use of images and info.
Written and researched by Meg McGath, 29 August 2012
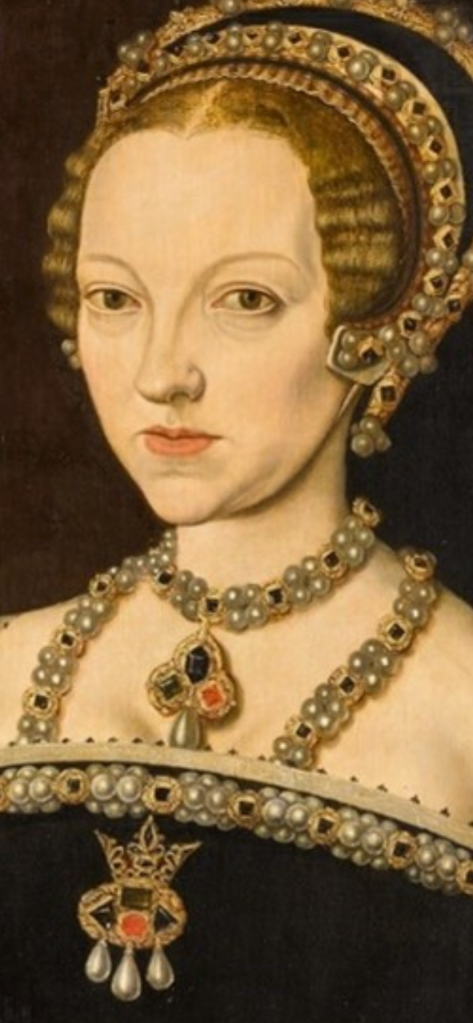
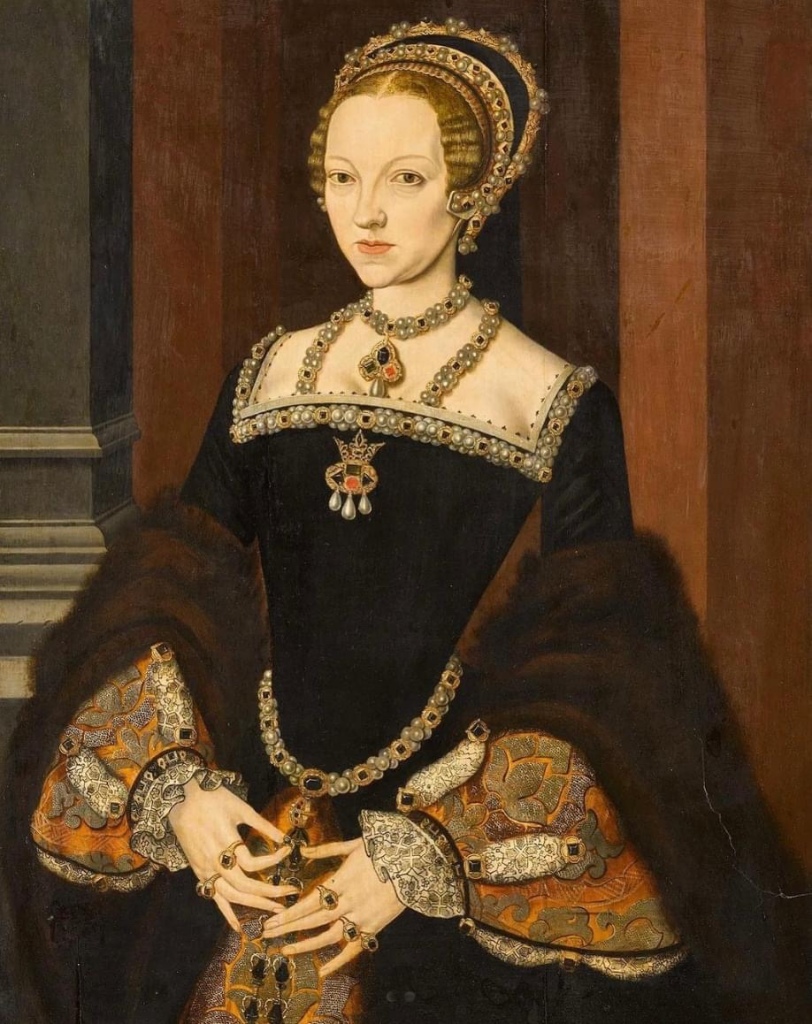
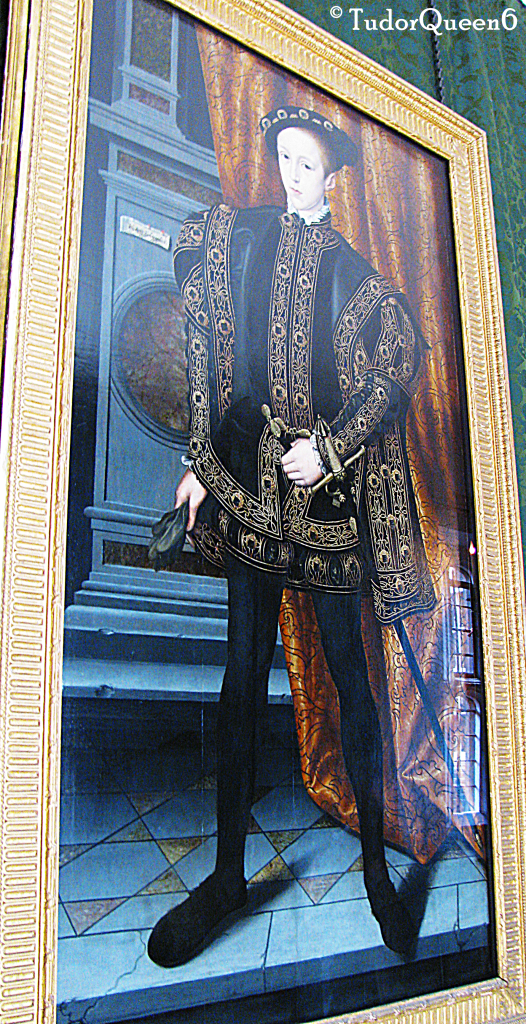




































![The nursery as it is today; the woman portrayed here is Queen Katherine's sister, Lady Anne Herbert [later Countess of Pembroke] who was Katherine's groom.](https://tudorqueen6.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/08/sudeley175.png)